What is subscription revenue recognition?
Cash flows differently for every business. Revenue recognition in a subscription business model can be challenging to understand, calculate, and report without all accountants following a revenue recognition standard.
Accounts receivable might be happy with the collection of payment for a one-year subscription, but to get an accurate picture of your business, you shouldn’t consider that revenue earned until you’ve fulfilled whatever their monthly subscription requires.
Revenue recognition, commonly known as rev rec, is a Generally Accepted Accounting Principle (GAAP) that specifies how and when you should recognize revenue. Accurate revenue recognition allows you to confidently gauge your company’s financial health and growth trajectory. Recognize revenue too early, and you’ll believe you have more to invest than you do; fail to recognize revenue correctly, and you may miss expansion opportunities. (Not to mention the income statements and other financial reporting requirements for public companies.)
The GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have revised their accounting standard on revenue recognition methods several times to improve the reporting of financial statements, with the latest requiring ASC 606 compliance.
ASC 606 standardizes how businesses define contracts with customers, how pricing and quoting are established, and how revenue for these is recognized. It follows a five-step process that identifies revenue streams, covering all money earned from contracts and the costs incurred throughout the customer lifecycle. This standard helps subscription businesses separate actual income from deferred revenue–and properly recognize income from an array of plan types, and customer contract modifications such as upgrades, downgrades, or cancellations.
In this article we’ve compiled the most frequently asked questions about revenue recognition for subscription businesses: what is it, how it works, why it’s important, and more. Let’s dive in!
What is the revenue recognition principle?
Rev rec is a Generally Accepted Accounting Principle (GAAP) that specifies how and when you recognize revenue, helping subscription businesses separate actual income from deferred revenue. This helps subscription companies properly recognize income from an array of plan types (monthly plans vs. yearly plans), or to account for plan modifications, upgrades, downgrades, or cancellations. The biggest issue for subscription-based businesses is “deferred-revenue” also called unearned revenue over time, namely the subscription period. That’s money essentially billed in their financial reporting but not considered revenue yet because the company hasn’t met the contractual obligations yet, as in the service hasn’t been rendered yet.
The revenue recognition principle is a key feature of accrual accounting that indicates that companies recognize revenue as it is earned as part of the payment terms, and not when they receive payments.
ASC 606: Setting the rules for rev rec in subscriptions
Back in 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606.
This new framework guides companies to recognize revenue from contracts with customers across different industries and business models. It affects all public and private companies that enter into contracts with customers, such as subscription-based businesses.
Five steps to recognize revenue with ASC 606
The ASC 606 five-step model replaces transaction-specific guidelines, establishing guidance and clarity through the revenue recognition process.
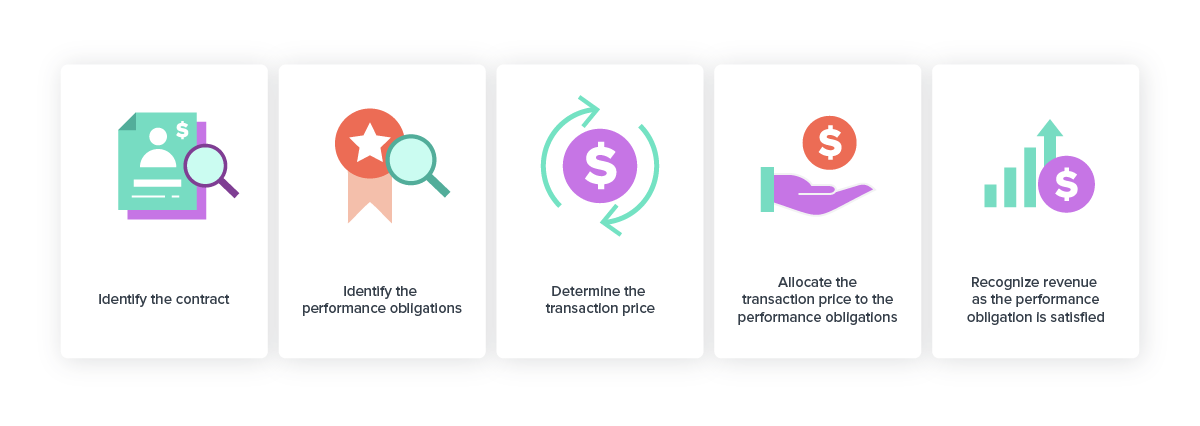
1. Identify the contract with a subscriber
This means any valuable contract that details the enforceable rights and obligations your business and consumer have agreed on. Under ASC 606, you don’t necessarily need a signed contract, as long as it:
Identifies each party’s rights
Defines payment terms
Has commercial substance
Specifies that collectibility is probable
States that all parties have approved the agreement and are committed to fulfilling their obligations
2. Identify the performance obligations
This refers to the promise of transferring goods or services to subscribers. Here you determine the different services to the consumer–considering they can be transferred independently of other performance obligations, and the subscriber can benefit from them.
Identifying these distinctions is crucial because a series of dependent service deliveries are considered just one performance obligation. However, a secondary subscription service would fall under a separate performance obligation if you can show a separate contract.
3. Determine the transaction price
Once you’ve established the obligations, calculate the transaction price of the contract. Include cash and non-cash considerations and other variable considerations, like discounts, add-ons, mid-cycle upgrades or downgrades, and any price concession your business offers.
4. Allocate the transaction price
Here's where subscription businesses show a different focus, where the product or service delivery is recurrent, making it a continuous performance obligation. You can split the total amount to be recognized as revenue for each performance obligation.
5. Recognize revenue
After you’ve outlined each contract with its obligations and financial values, all that's left is to start recognizing revenue as you serve your customers.
While the ASC 606 framework seems simple, implementing it can be challenging. Under ASC 606, revenue is recognized when contractual obligations are met, not when the payment is made–changing the game for subscription businesses
When should revenue be recorded in subscriptions?
Contrary to traditional models where service delivery happens at the transaction moment, subscription-based businesses recognize revenue when the cash payments have been earned and not just collected. In this case, any unmet balance will remain on a balance sheet as accounts receivable from the initial sale date until the date the customer makes a payment.
Revenue recognition example
Membership revenue recognition is easiest to understand when customers pay upfront, like in the case of annual subscriptions. Let’s consider a wine club that offers a $480 annual plan for subscribers to receive three bottles of wine every month. It’s a monthly service with a subscription fee paid annually.
When do you recognize revenue? The answer is $480 annually divided by 12 months, which comes out to $40 of recognized revenue every month. Just because $480 has been paid from the get-go doesn’t mean you’ve earned every penny of that amount. The generally accepted accounting practice in a subscription model is to recognize revenue over a period of time.For example, if the subscription had to be canceled before that year was up, you would technically owe money to that customer.
Why is revenue recognition important for subscription billing?
Taking into consideration balance sheets to income and financial statements, revenue recognition offers transparency into some of the most important aspects of any business. Accurate membership rev rec lets you confidently speak about your subscription business’ performance and growth trajectory.
However, failing to recognize revenue correctly may lead to missed opportunities to grow your business. Recognize revenue too early, and you may think you have more to invest than you do.
Check this out: Everything you need to know about ASC 606 revenue recognition for subscription businesses.
How do successful subscription businesses ensure accurate revenue recognition?
Subscription revenue recognition is more unique than most people’s basic understanding of rev rec. Recurring revenue, while reliable and stable revenue generation for subscription companies, makes a strong case for the time revenue is earned versus collected, especially with different subscription plans.
A revenue recognition platform is key for accurate, timely subscription accounting and monitoring financial performance correctly. Successful subscription brands–from membership sites to software companies to online publications–automate and streamline processes to minimize errors and ensure compliance with subscriptions in accounting ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards.
Make ASC 606 compliance easy
Take the stress out of compliance challenges with compelling revenue recognition software. Your subscription management and recurring billing platform should be your source of truth. Recurly’s revenue recognition solution simplifies ASC 606 and IFRS 15 reporting processes, helping you
Lower costs and streamline your tech stack with numerous accounting standards that better connect your billing and revenue management processes.
Improve revenue visibility, reporting accuracy, and predictability with real-time, multi-dimensional revenue insights, reporting, and forecasting.
Accelerate your financial close with end-to-end revenue automation that delivers the metrics you need to speed up financial close.
Reduce compliance risk with automated workflows that meet the defined ASC 606 five-step model.
Remove barriers to scale with a fully configurable solution that supports your specific business requirements.
Partnering with the right subscription management and recurring billing platform can be a game-changer in revenue recognition. With Recurly, revenue recognition is automated, fast, and accurate.
Learn how Recurly Revenue Recognition can help you meet your subscription business compliance needs.
Recurly’s Revenue Recognition ensures streamlined and automated compliance with multiple revenue reporting standards with an enterprise-grade, fully configurable solution. Our solution allows you to access a revenue schedule export for faster, more accurate subscription accounting.